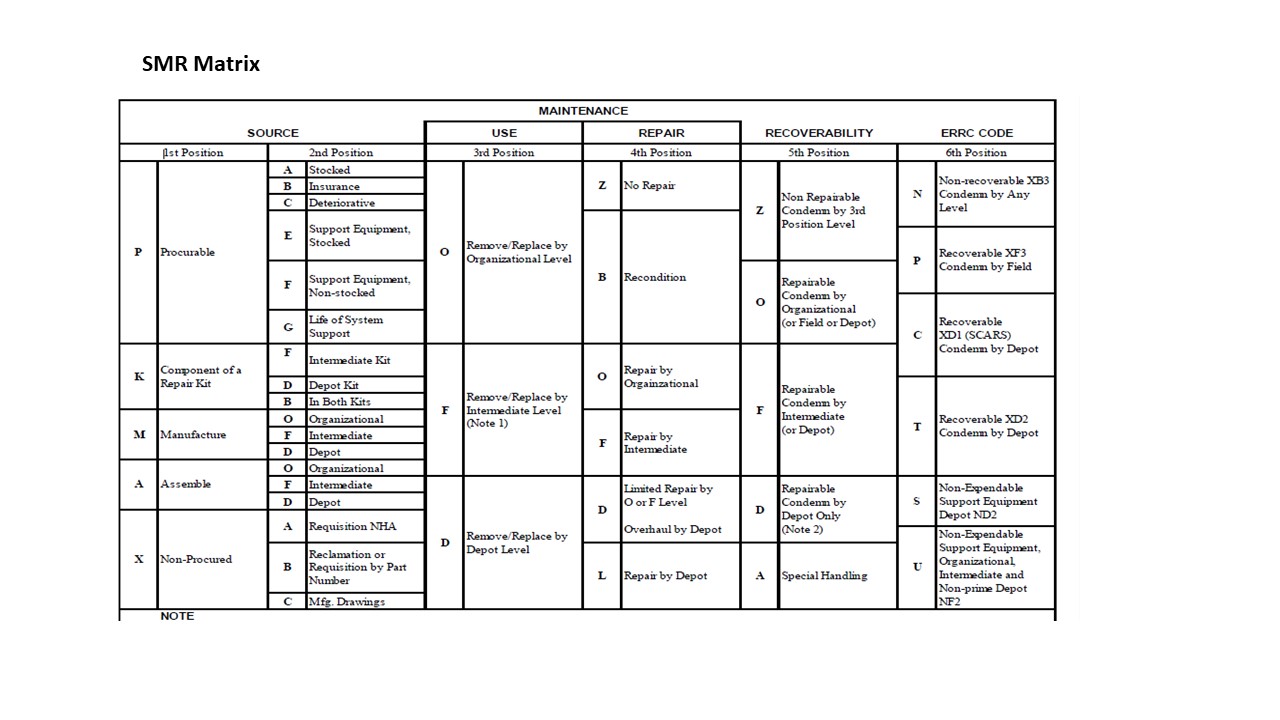
A typical SMR Code position activity matrix is provided here.
 Contact us for more details:email Adrian Stephan
Contact us for more details:email Adrian Stephan
A typical SM&R code is PACLZA which translates to:
For current information about this service please email Adrian Stephan to request information.
Source, Maintenance and Recoverability (SMR) is a logic of coding parts to align and synchronise (harmonise)their source (acquisition), maintenance,support,and disposition activities. It was developed by the US Defense and is documented in several military documents such as US Army Regulation 700-82 and US military standards (MIL-STDs) such as Logistic Support Analysis Record (LSAR) MIL-STD-1388-2B. It is defined by Data Element Dictionary (DED) 389 in MIL-STD-1388-2B.as follows.
DED 389 SOURCE, MAINTENANCE AND RECOVERABILITY CODE (SMR) 6 X L -
SMR codes are a series of alpha or alphanumeric symbols used at the time of provisioning to indicate the source of supply of an item, its maintenance implications, and recoverability characteristics. The provisioning activity may require the contractor to recommend these codes. Approved codes are defined in: AR 700-82; OPNAVINST 4410.2; AFR 66-45; MCO 4400.120; and, DSAR 4100.6.
SE SOURCE, MAINTENANCE AND RECOVERABILITY CODE. The SMR of the support equipment under analysis.
Although the SMR Code has a formal structure, our approach is to add additional codes to suit situated practies as they are needed. A short description of the situated code is below.
The standard SMR code has the following general structure:
A typical SMR Code position activity matrix is provided here.
 Contact us for more details:email Adrian Stephan
Contact us for more details:email Adrian Stephan
A typical SM&R code is PACLZA which translates to:
As can be seen, the code enables simplification of Item management activity description. It is necessary to be diligent to make sure coding and activities are harmonised to meet requirements.
The importance of item economics using SMR cannot be overstated; it is an essential item control and decision making activity.
The SMR Code is a pivotal process for machine acquisition and support. Machine support is not a self-actuating process. It is a complex interaction of systems: human, production, technology, operations, and machinery. If a machine support program is to deliver effective and efficient maintenance, these systems must be harmonised and at their peak performance. Managing maintenance is about how to get all of these systems working together and in an optimised manner. No matter how good the maintenance management tools are, unless they are managed correctly and efficiently they are of limited benefit. A significant aspect of maintenance systems is to address the losses and waste in terms of time, money and opportunities. Waste is often the hidden cost and not measured in the performance goals of maintenance management. This SMR program takes a lean approach to machine support systems. i.e. It first looks at the maintenance management processes and then addresses the management of waste and lossess other in those maintenance processes.
SMR is a method that uses standard methods in a combined arrangement to evaluate the effectiveness of the item. The outcome is a triplet measure of logistics effectiveness. The advantage of an SMR is that it can be done quickly and provide a historic trail of effectiveness of the logistics systems to maintain machines.
The situated code (SSMR) is developed to meet the overall analytical requirements of the program and the equipment. SSMR can be considered as a tailored solution to the situation. It includes, but is not limited to, elements such as:
As these elements will usually have indeterminate relationships they are determined on a situation by situation basis, discuss your specific needs with us. Contact email Adrian Stephan to discuss your requirements so that we understand them and propose solution options.
We provide training and analysis services to work with clients to develop a Source, Maintenance and Recoverability Code in two parts. The first part is the classic SMR and the second part is the tailoring to suit a situated evnironment. That is, to seek and align the competitive advantage of the organization to the Foundations of Operations. This SMR alignment sets in place subsequent performance measures such as capability, dependability and durability to achieve competitive advantage. We can help you code sustainability, threat, vulnerability, and resilience factors.That is, a closed loop system to achieve the competitive advantage with the SMR plan as the cornerstone plan.
We work with you to develop these key SMR plans to achieve operations.
For information about this service please email Adrian Stephan to request information.